Renewable Natural Gas

Renewable natural gas for power generation and transportation applications using various waste streams – biogas from wastewater plants, dairies and landfills, and food waste – is a very attractive negative emissions opportunity. The InnoSepra biogas upgrading technology provides a very cost-effective solution to convert raw biogas to high purity renewable natural gas. It has the potential for reducing the gas upgrading cost by more than 30% and the energy required for upgrading by more than 45%. The technology produces high purity natural gas (>98% purity) at a very high recovery (>98%) and has been demonstrated both with dairy biogas and landfill gas. With renewable energy credits available in many parts of the United States the use of biogas upgraded with the InnoSepra Process can provide very attractive returns for various stakeholders.

Renewable Natural Gas Technologies
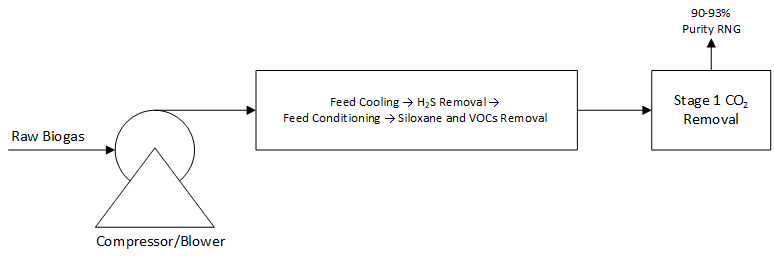
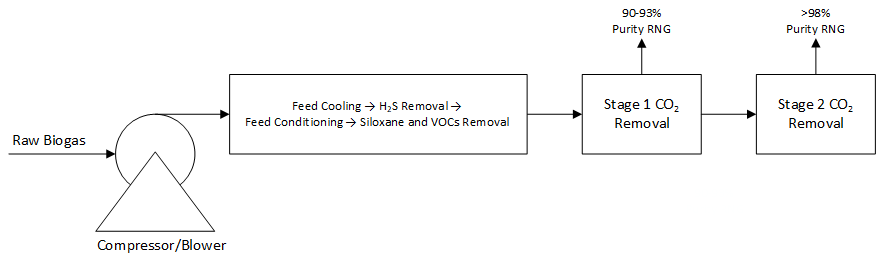
The InnoSepra Renewable Natural Gas Technologies include technologies for removal of siloxanes and VOCs, technologies for producing 90-93% purity gas suitable for on-site power generation and CNG, and technologies for producing pipeline quality gas at very high recovery. These technologies have lower operating cost, capital cost, and CI (Carbon Intensity) Score compared to current gas upgrading technologies. Most of these technologies can be used for both new plants as well as existing plants.

Removal of Siloxanes and VOCs
In addition to the removal of hydrogen sulfide, all biogas and landfill gas projects require removal of siloxanes and VOCs prior to removal of carbon dioxide. Most commonly used siloxane and VOC removal technology involves refrigeration cooling of compressed gas to a temperature between 5-10°C, dropping out condensed water and reheating to 20-25°C to reduce the relative humidity to below 40%. This is followed by adsorptive removal of siloxane and VOCs. The InnoSepra siloxanes and VOCs removal technology can dry the compressed gas to a relative humidity below 5% prior to removal. This increases the capacity for siloxanes and VOCs by 2-4 X. Depending on the level of siloxanes and VOCs in the feed, this could have a significant impact on the operating cost. The technology is retrofittable to existing biogas and landfill gas plants.

Gas Upgrading for Power Generation and CNG
Typical power generation projects utilizing biogas and landfill gas only remove siloxanes and H2S prior to power generation. This requires the use the of a high capital, high maintenance and lower efficiency biogas engine. The InnoSepra technology provides a very cost-effective option for removing H2S and siloxanes and producing a gas stream containing 90-93% methane. This gas is suitable for the use of a lower capital, higher efficiency and a lower maintenance natural gas engine. Analysis by InnoSepra indicates that cost of power generation using this gas is at least 20-25% lower than cost of power generation using a biogas engine. While the 90-93% purity gas cannot be injected into a natural gas pipeline it is suitable for local use in heavy duty vehicle such as school buses and garbage trucks after they have been retrofitted with natural gas engine. The payback time in this application is less than 2 years.

Gas Upgrading for Renewable Natural Gas
Renewable natural gas for pipeline injection requires a methane purity greater than 98% in addition to meeting specifications on various other impurities. Membrane based upgrading is the dominant current technology for biogas and landfill gas upgrading followed by Pressure Swing Adsorption to a smaller extent. The membrane-based upgrading technology is very energy intensive needing between 0.55-0.60 KWh/nm3 of electrical energy. The InnoSepra biogas upgrading technology can upgrade biogas to a purity greater than 98% by providing more than 98% recovery. The energy requirement is at least 45% lower than membrane-based upgrading technology. The lower energy intensity of upgrading leads to at least a 30 point lower CI Score.

Renewable Natural Gas Markets
The Renewable Natural Gas Markets fall into two main categories; those targeting LCFS (Low Carbon Fuel Standards) credits, and those targeting Cellulosic RINs. The LCFS credits provide the highest value but also require lowest carbon intensity. Cellulosic RINs provide lower value and are less dependent on CI Score, but do require the lowest production cost. The InnoSepra technologies can address both these markets and can also be retrofitted to improve the CI Score of the existing projects.

Renewable Natural Gas Demonstrations
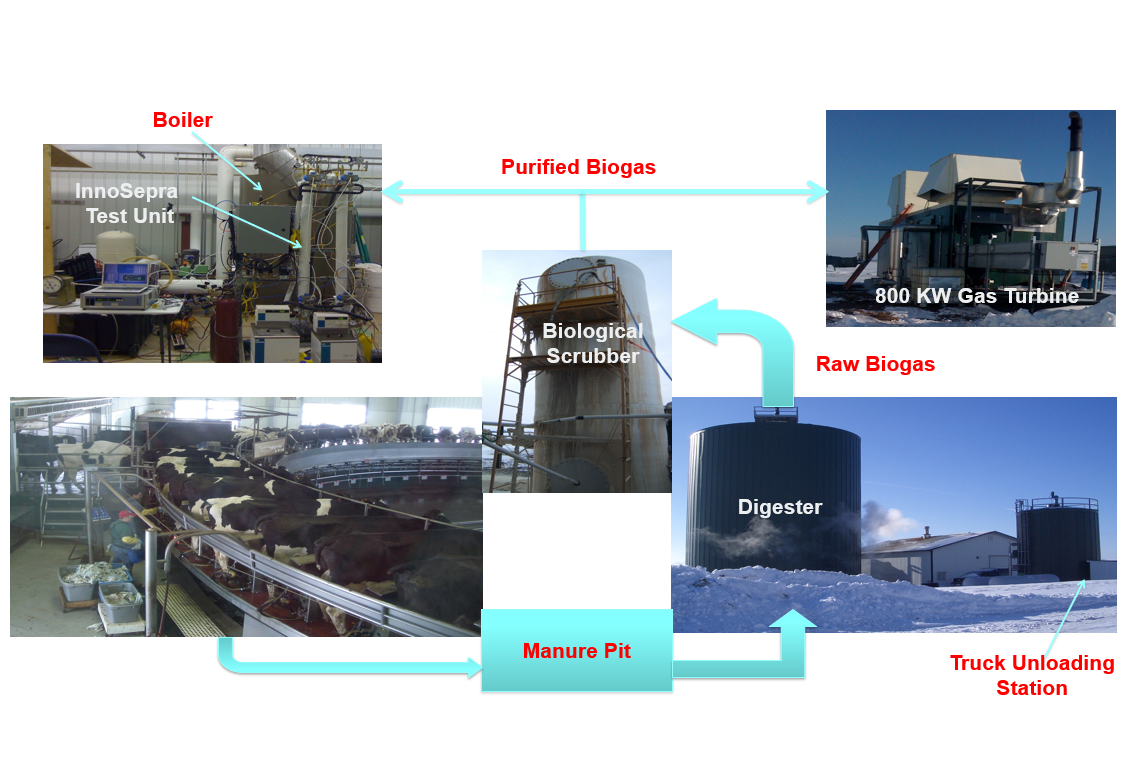
Lab Scale Testing at a Dairy Farm
The first test of InnoSepra process was done at lab scale at a dairy farm in Wisconsin. The demonstration with a feed containing about 60% methane and about 1,000 ppm hydrogen sulfide showed the technology can produce over 99% purity methane with a recovery of over 98%. A techno-economic analysis showed at least 35% lower upgrading cost compared to technologies available at that time.

Pilot Scale Testing at Simi Valley Landfill
Pilot Scale Demonstration at Waste Management’s Simi Valley Landfill showed that the InnoSepra technology can produce a methane product with less than 2% CO2 and less than 1 ppm of hydrogen sulfide and moisture. The CO2 removal was more than 98% and methane recovery was over 98%. A techno-economic analysis showed that the gas upgrading cost was at least 40% lower than PSA and Membrane technologies.

Renewable Natural Gas Value Proposition
The InnoSepra technology has both a lower cost of upgrading and lower carbon intensity of upgrading. It can address both the LCFS (Low Carbon Fuel Standard) markets in California, Washington and Oregon as well as D3 and D5 RINs markets. Due to lower energy required for gas upgrading it can reduce the carbon intensity of any LCFS project by more than 30 points which results in a higher value for the RNG sold in this market. The InnoSepra technology also has at least 30% lower gas upgrading cost (>$3/MMBTU reduction in upgrading cost). This results in higher returns for project developers when the gas in sold to generate RINs as well as to generate carbon credits in voluntary markets. It also makes the projects less susceptible to volatility in RIN pricing.